Healthy Eating Recommendations for Thyroid Control

Thyroid glands are the most important part of our endocrine system; this gland is responsible for regulating everything starting from our mood, to weight, our body temperature, metabolism and digestion.
Our thyroid gland acts as a modulator and is susceptible to the cause and effects of our actions. Therefore, they can quickly go off-balance in no time.
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the body is unable to make enough thyroid hormones. This can slow down your body’s metabolism.
Nearly 1-2% of the worldwide population is affected by hypothyroidism and women are ten times more likely to be impacted by it than men.
How Does Thyroid Function in our Body?
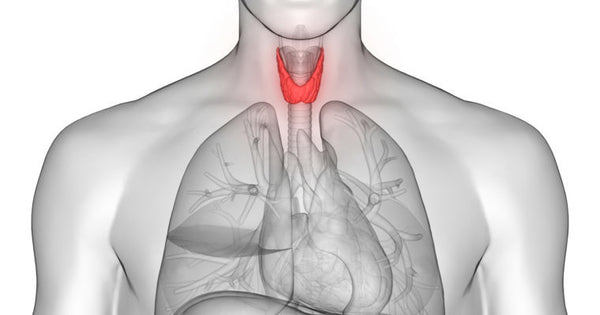
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland found at the front of our throats just below the Adam’s apple. The main function of thyroid glands is to create thyroid hormones, T4 and T3. T3 and T4 are then released into and blood where they take care of our body’s temperature, metabolism, heart rate, muscle control, bone maintenance and brain development.
The release of these hormones is controlled by the TSH (Thyroid-stimulating hormone) produced by the pituitary gland. The body utilizes them to assist with energy flow and to monitor other hormonal functions.
Effects of Thyroids

An estimated 30million people are expected to suffer from some kind of thyroid disorder.
Under normal conditions, thyroid releases just the right amount of hormones so that TSH levels remain constant. But in some cases, this mechanism can get affected causing the thyroid levels to malfunction. The two most commonly observed conditions are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Those suffering from an underactive thyroid condition are known as hypothyroidism while the ones facing an overactive thyroid disorder is called hyperthyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism or over stimulation of thyroid hormones can result in increased heart rate, anxious states and weight loss.
While hypothyroidism or lack of thyroid hormones slows down the body’s mechanism, cause sluggishness, weight gain, heart complications and depressive states.
A severe form of thyroid disorder can cause Hashimoto’s and Graves’s disease. Hashimoto is a condition in which the body recognises thyroid antigens and foreign and starts attacking them.
Treatment and Diagnosis

Diagnosis is usually made by specialist and confirmed by laboratory tests only for TSH, T3 and T4.
Medications usually contain synthetic or animal-derived thyroid hormones that replace the ones that aren’t produced by the body and can contain only T3 or T4 or a combination of T3 and T4 or both depending upon the deficiency.
Nutrients Required for a Healthy Thyroid

Iodine is one of the main nutrients needed for a well-functioning thyroid. However, one should be careful as too much of it can pose problems and lead to hypothyroidism. Therefore, it’s advisable to consult a health practitioner before taking iodine supplements.
Tyrosine is another important nutrient required for thyroid formation. Our bodies are capable of manufacturing tyrosine from amino acids, but dietary tyrosine is also important and can be found in peanuts, almonds, banana, line beans, avocados, pumpkin seeds and sesame seeds.
Other important nutrients essential for the proper functioning of thyroid hormones are vitamin B, clean sources of fats, a good amount of amino acids, and a variety of fruits and vegetables that give supply high-quality natural vitamins and minerals.
Zinc and copper are two such minerals that are necessary for the conversion of T4 to T3. Plant sources include sunflower and pumpkin seeds, squash seeds, spinach, cacao, beans, mushrooms, spirulina, cashews and avocado.
Nutrients that are Harmful

Other than eating varied foods that support a healthy level of the thyroid, one should look out for foods that might reverse the effect. One such food group is known as goitrogens.
Foods containing goitrogens are recommended to be avoided since these compounds tend to block iodine absorption, which could turn out to be a major issue if you’re iodine deficient.
They get their name from the term goitre, which results in an enlarged thyroid gland that may occur with hypothyroidism. However, this is something that was more common back in the days when there was limited knowledge about keeping thyroid in check. Nowadays, it occurs more rarely.
Foods that contain goitrogens are (21Trusted Source):
- Soy foods: tofu, edamame, tempeh
- Vegetables like: cabbage, broccoli, kale, cauliflower, spinach, etc.
- Fruits and starchy plants: sweet potatoes, peaches, strawberries, etc.
- Nuts and seeds: millet, pine nuts, peanuts, etc.
One way to avoid the harmful effects of goitrogenic compounds is to steam your cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, kale, mustard, turnips and cook or roast your beans, nuts and millet properly before consuming so that the goitrogenic compounds can be highly reduced.
What Foods to Avoid for Hypothyroidism?

Thankfully one doesn’t need to avoid many foods when suffering from hypothyroidism.
But definitely, avoid highly processed foods, because of their high-calorie intake. This can aggravate your weight if you already have hypothyroidism.
Here are the foods one must avoid:
- Millets: all varieties of them
- Highly processed foods: Cakes, Cookies, Hot dogs, etc.
- Supplements: Selenium and Iodine are essential for thyroid health but getting too much of them may cause significant harm. Only get the supplement when instructed by healthcare professionals.
What Foods to Consume for hypothyroidism?
- All vegetables – including cruciferous vegetables are fine to eat in moderation.
- All fruits including berries, bananas, oranges, tomato etc.
- Gluten-free grains like rice, quinoa, chia seeds and flax seeds.
- All beverages other than non-caffeinated beverages
Alternatively, you can also include PLIX plant protein powder in your diet which is a great source of vegan protein and other plant-based proteins.
You can also buy our Plant-based protein powder from Amazon here: